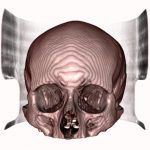
Differences Between FDM and Polyjet 3D Printing Technology when 3D printing DICOM files
Any business that relies on prototype and design elements have now taken advantage of 3D printing technology. Thanks to the continued increase of advancement in technology, we are now capable of 3D printing complex structures and models using a printer. This is with the help of special computer-aided design (CAD) software which slices the model into layers that the printer will print one by one until the physical model is produced.
We use two 3D printing technologies or additive manufacturing (AM) processes; Fused Deposition Modelling or FDM and Polyjet. Whilst they both offer to produce accurate3D models that are great for surgical planning, these two technology platforms remain distinct and present different benefits.
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
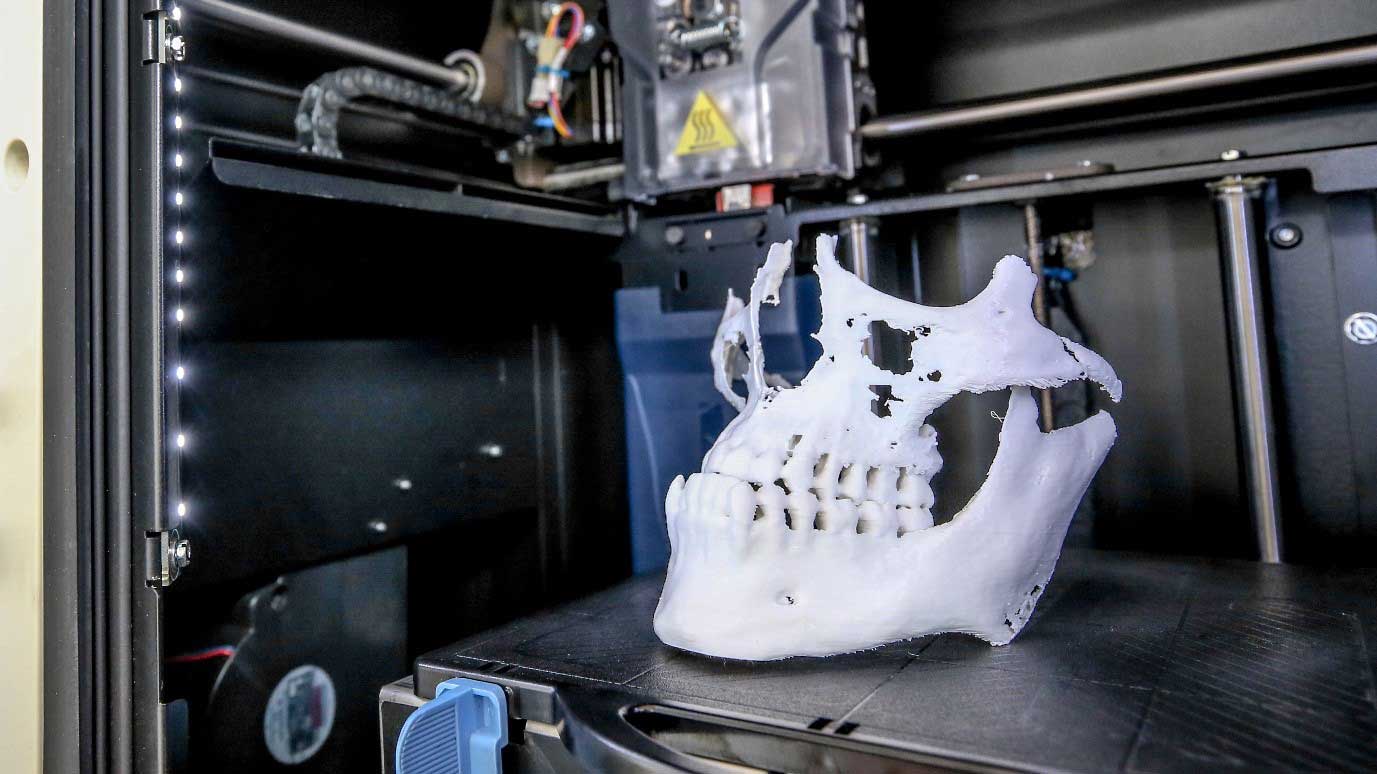
With Fused Deposition Modelling or FDM, a thermoplastic filament is melted down and extruded from a print head and once extruded into a bead, the material is immediately set as it cools in the machine and layered on the build platform. The process of extruding and melting is repeated layer by layer until the part is complete. FDM uses two types of materials:
- The modelling material which becomes the finished product.
- The support material which works as a scaffolding.
Once the model is removed from the machine, the support material can be removed by either breaking it off or by using a detergent and water to dissolve it. This allows for very intricate internal cavities and undercuts to be created without the risk of breaking.
The toughness of the ABS material used in FDM 3D printing makes it an ideal material for cutting and drilling and also for bending plates around.

Polyjet 3D Printing
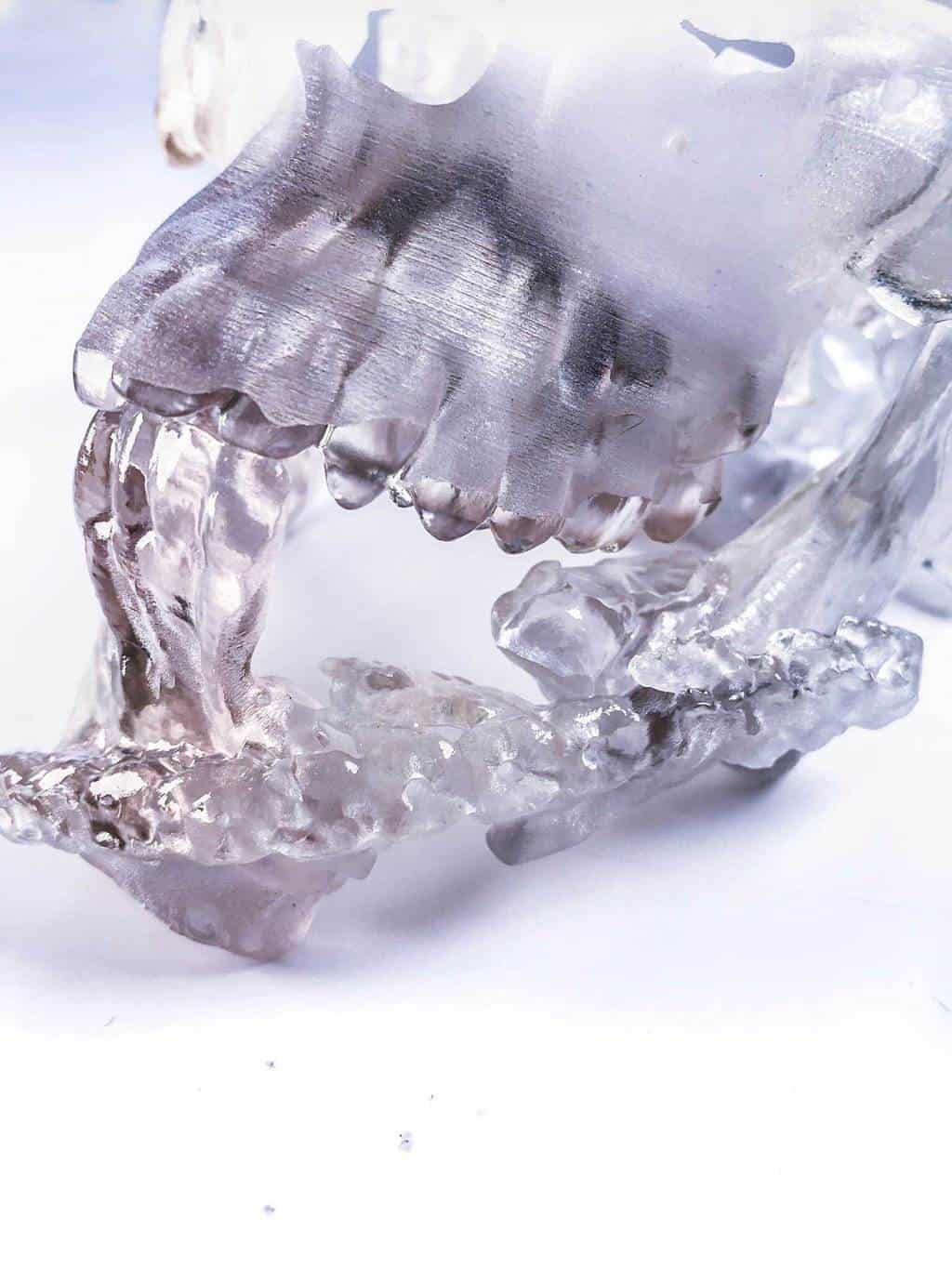
The Polyjet process involves a carriage with four or more inkjet heads and ultraviolet (UV) lamps that deposit tiny droplets of photopolymer resinthat solidify when exposed to UV light. The complete 3D object is formed after a repeated printing of thin (16μm) layers of material. The support material for this process is a gel-like substance which can be removed easily by washing it off with water. The completed model requires no additional curing or processing.
This process allows for exceptional detail and accuracy and dissolvable support material means even the thinnest and most intricate details can be printed without risk of breaking.
Polyjet also allows for the combination of materials and colours to differentiate between areas of interest. Nerves, implants and other structures can be produced in contrasting colours to help with procedure planning.
Choosing the best option for you depends on how the part will be used. Let’s take a closer look as to how these two technology platforms differ from each other:
Application
Whilst Polyjet has the ability to create parts with exceptional detail and multiple materials, FDM prides itself on the ability to produce durable parts that are ready for end-use applications. If toughness and mechanical strength are critical to your part and detail is less important, FDM may be the best choice. FDM is also approximately half of the cost of Polyjet.
Material
To satisfy your part’s application, it is also important to think of what material is needed. Polyjet can print parts with a variety of colours and shore harnesnees and has the option to blend multiple digital materials within the printing process. On the other hand, even though FDM isn’t capable of producing flexible parts, you have the ability to print more quickly and at lower cost.
Surface Finish
The surface finish and aesthetics can be crucial especially when planning complex cases or when explaining a procedure to a patient. FDM can produce parts with complex geometries and intricate components. However, Polyjet offers greater realism, smooth surfaces and fine feature detail by the use of liquid photopolymers, which are jetted in liquid form and then cured through exposure to ultraviolet light.
Durability
Polyjet parts can sometimes deteriorate with prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light whilst an FDM product will be more dimensionally stable. Additionally, polyjet prints are more brittle whereas FDM is tough and more suitable to print parts that require mechanical strength or UV/Thermal stability.
Part Size
Another factor to consider when choosing a technology platform between these two is the size of the part. Whilst PolyJet and FDM both offer similar dimensions for the part size, FDM technology tends to be more cost effective for larger models such as skulls etc.
Medimodel combines expertise in medical imaging and cutting edge 3D printing processes. If you are interested in finding out more or discussing your case, you can contact us on +44(0)117 325 8171.